What is a diabetes A1C test? The hemoglobin A1C is a blood test that is a regular part of diabetic care. It is done every 3-4 months. The benefit of the A1C test is that it provides a measure of how your blood glucose levels have averaged over the past 2-3 months and provides a “picture” of overall blood sugar control. Sugar builds up in your blood and combines with your hemoglobin, becoming “glycated,” the average amount of sugar in your blood can be found by measuring your hemoglobin A1c level.
The daily blood glucose checks that are done at home or in the doctor’s office measure the blood glucose level at that moment. The A1C test measures the blood sugar over time and is extremely important for monitoring how well your diabetes is controlled.
For people without diabetes, the normal range for the hemoglobin A1c test is between 4% and 5.6%. Hemoglobin A1c levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate increased risk of diabetes, and levels of 6.5% or higher indicate diabetes. Because studies have repeatedly shown that out-of-control diabetes results in complications from the disease, the goal for people with diabetes is a hemoglobin A1c less than 7%. The higher the hemoglobin A1c, the higher the risks of developing complications related to diabetes.
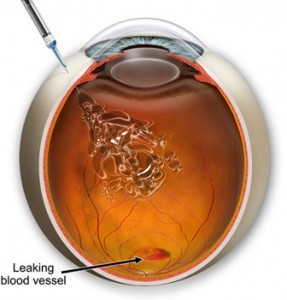
One of these complications due to high blood sugar is diabetic retinopathy. Since diabetes primarily affects the blood vessels, it is very important to have a dilated eye examination at least once a year. The retina inside the eye is the only place in the body where blood vessels can easily be examined.

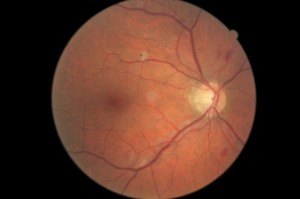 retinopathy.
retinopathy.